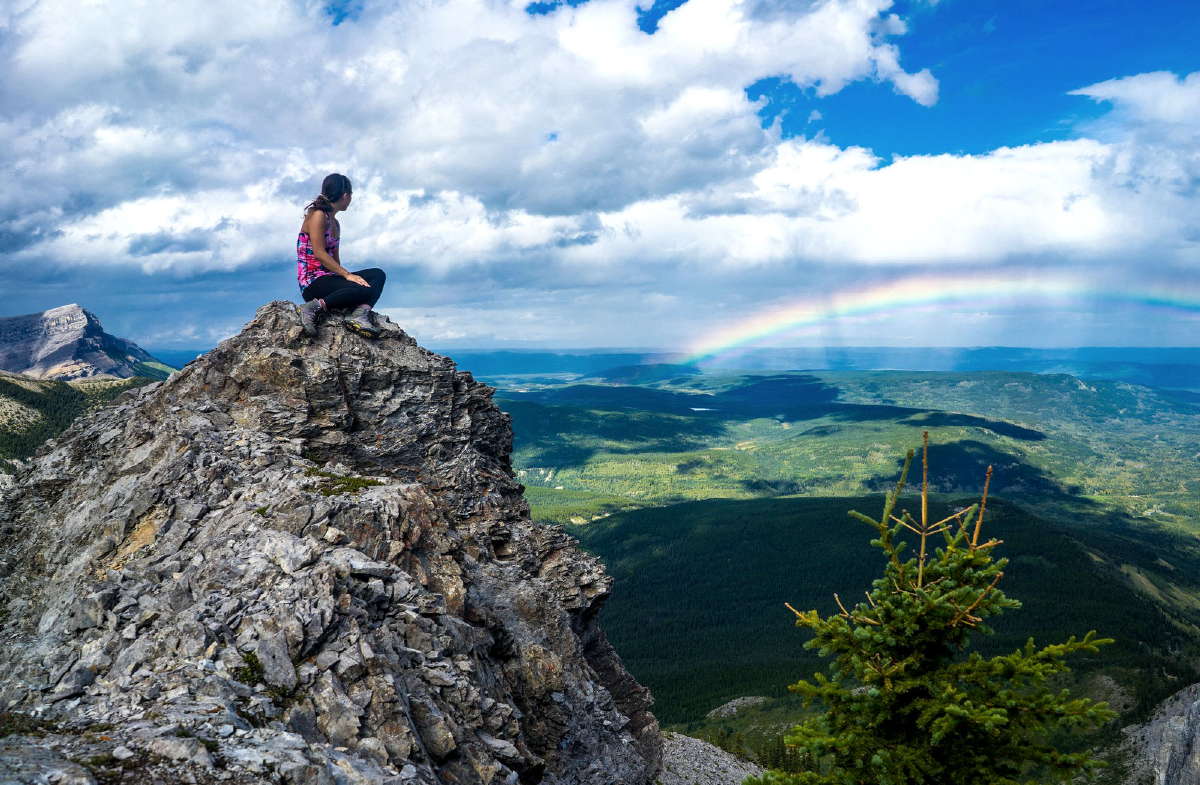
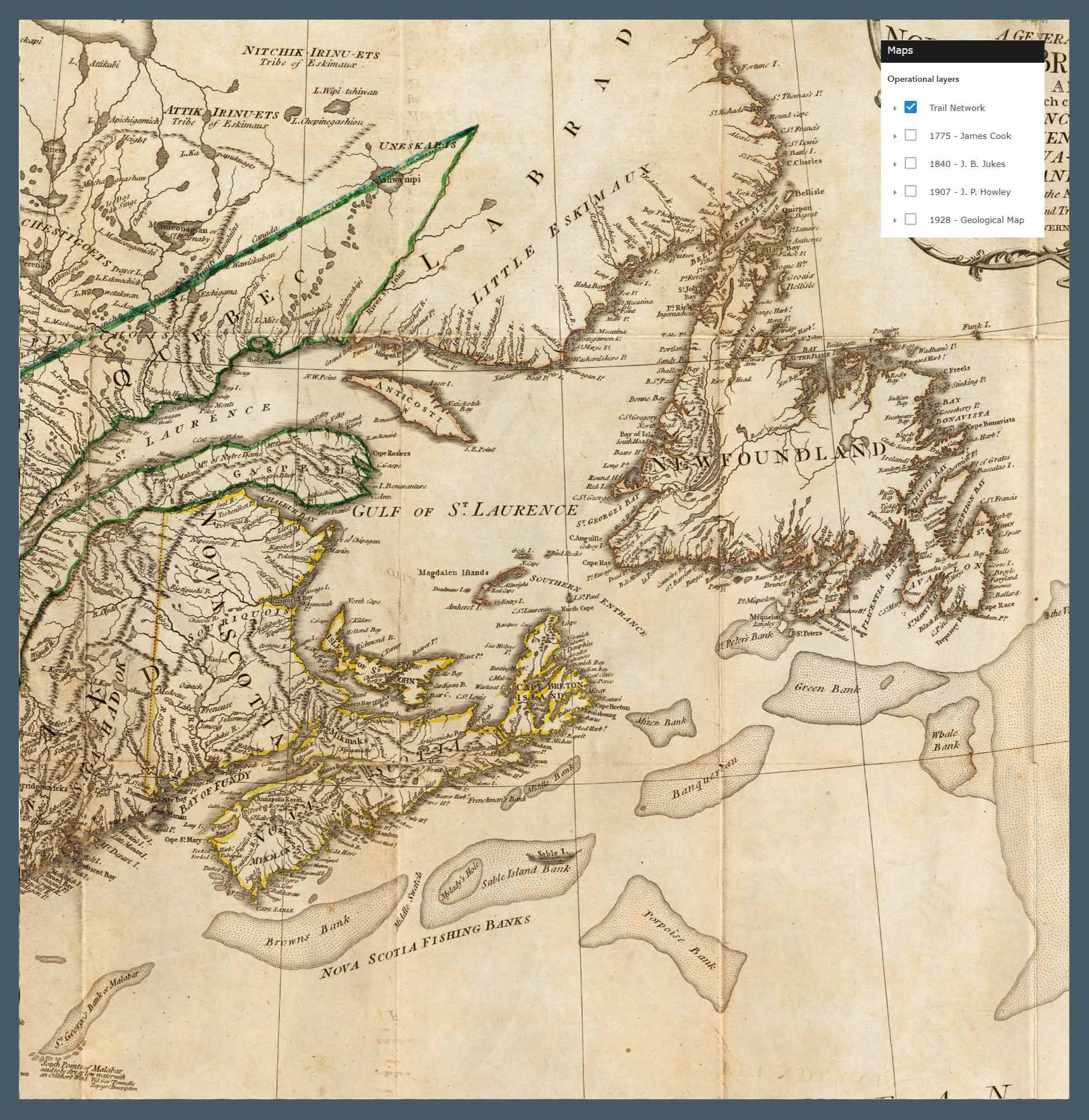
The Appalachian-Caledonian Corridor spans eastern North America, Western Europe, and North Africa, and represents a complex amalgamation of ancient tectonic events. It is also characterized by diverse communities of people and cultures. In North America, Native American tribes, including the Cherokee, Mohawk and Mi’kmaw, have a rich history that contributes to its cultural tapestry. European settlers later established Appalachian traditions, with Scotch-Irish, German and French immigrants leaving lasting influences on the music, folklore, and dialects of the area.
People
The Caledonian Mountains of Europe, primarily in Ireland, Scotland and Scandinavia, have a unique cultural identify that includes Celtic and Norse heritage. On the Iberian Peninsula, Spain and Portugal includes a myriad of cultural influences, from the original Iberian and Celtic heritage to Latin and Arab traditions. In North Africa, a blending of the indigenous Berber culture with Arab and French influences has shaped the identity of Moroccan communities.
Throughout the A-C corridor, economic activities vary, with agriculture, forestry, and tourism playing crucial roles. The natural beauty of the mountains attracts outdoor enthusiasts, while historical sites and cultural events contribute to tourism. Challenges such as environmental conservation, economic development, and preserving cultural heritage are common concerns for people all along the corridor.
The Appalachian-Caledonian Corridor is not only a geological phenomenon but also a diverse tapestry of cultures and histories that share a connection rooted in the ancient geological events that shaped their landscapes. The corridor stands as a testament to the interplay between geology and human civilization across continents.
[Source: ChatGPT]