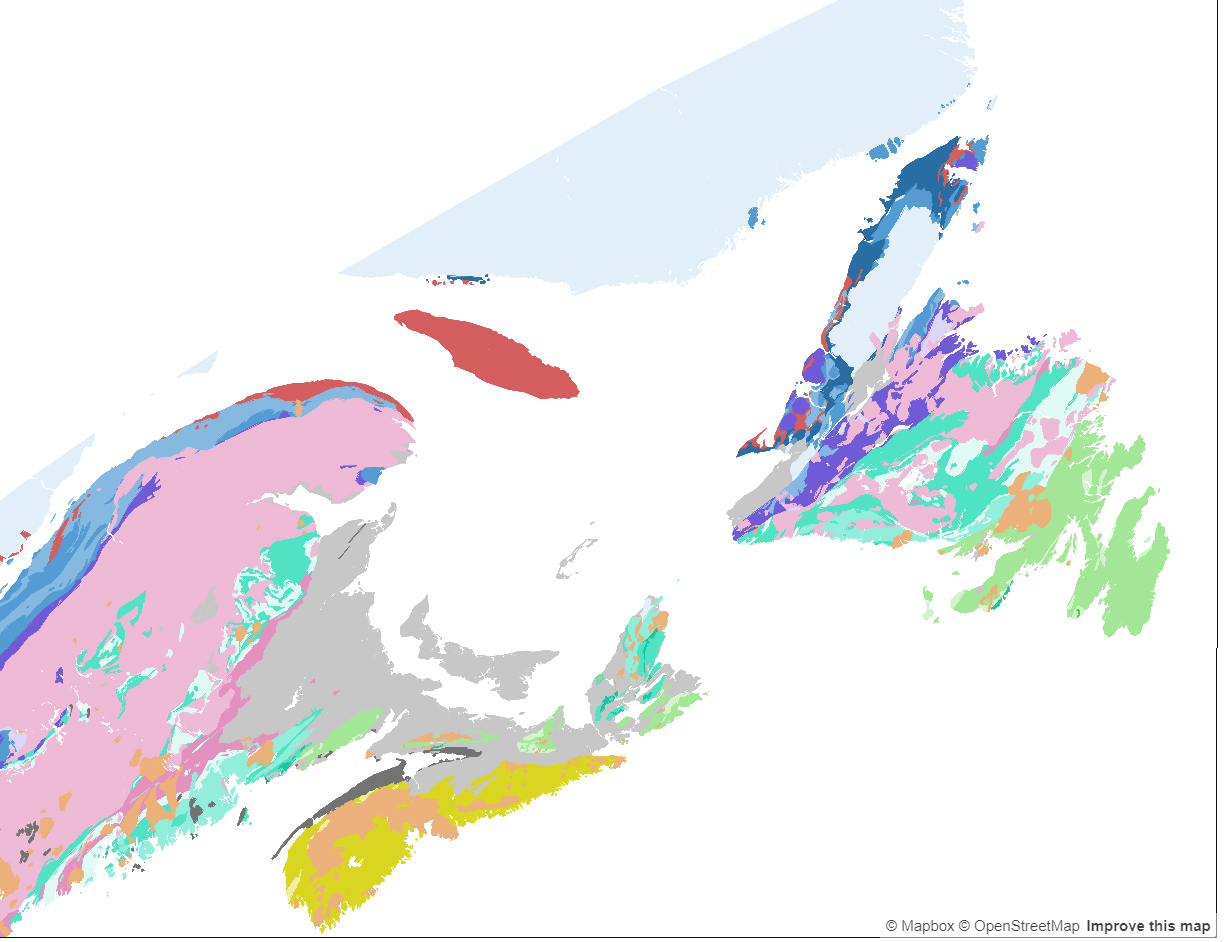
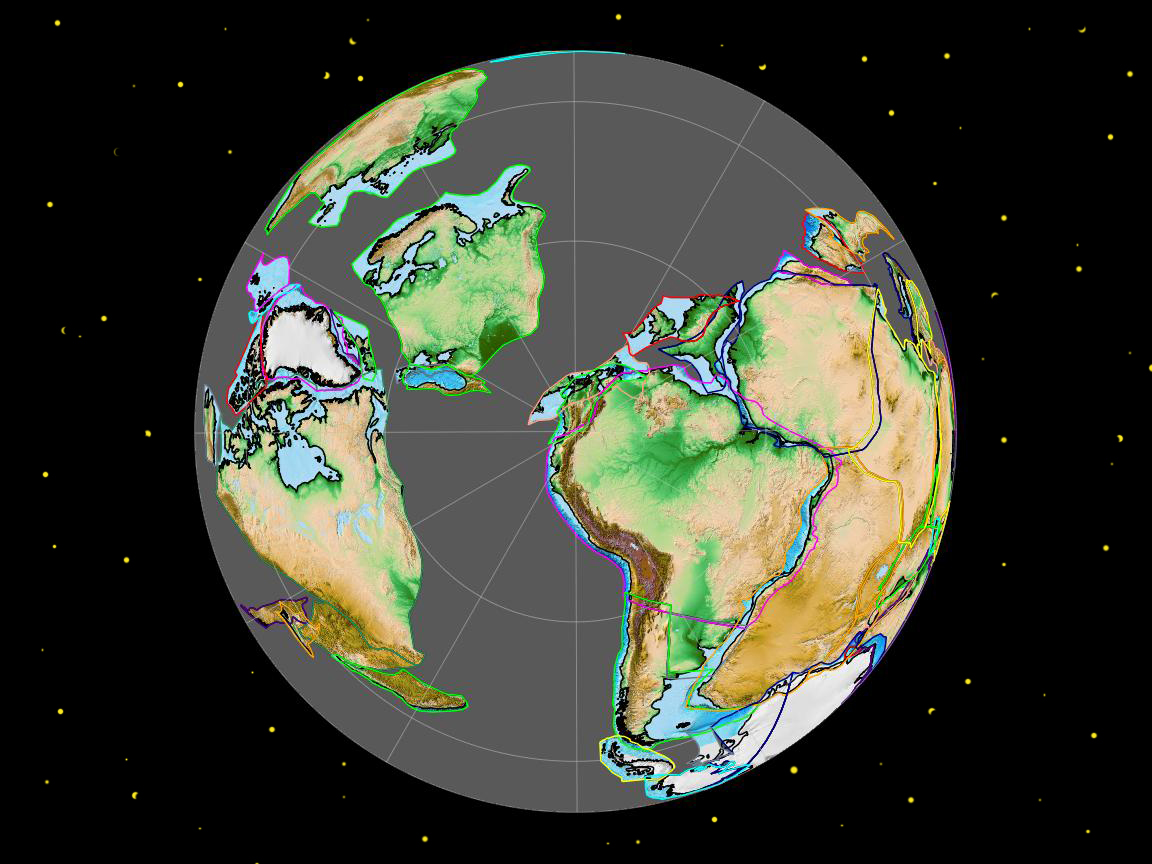
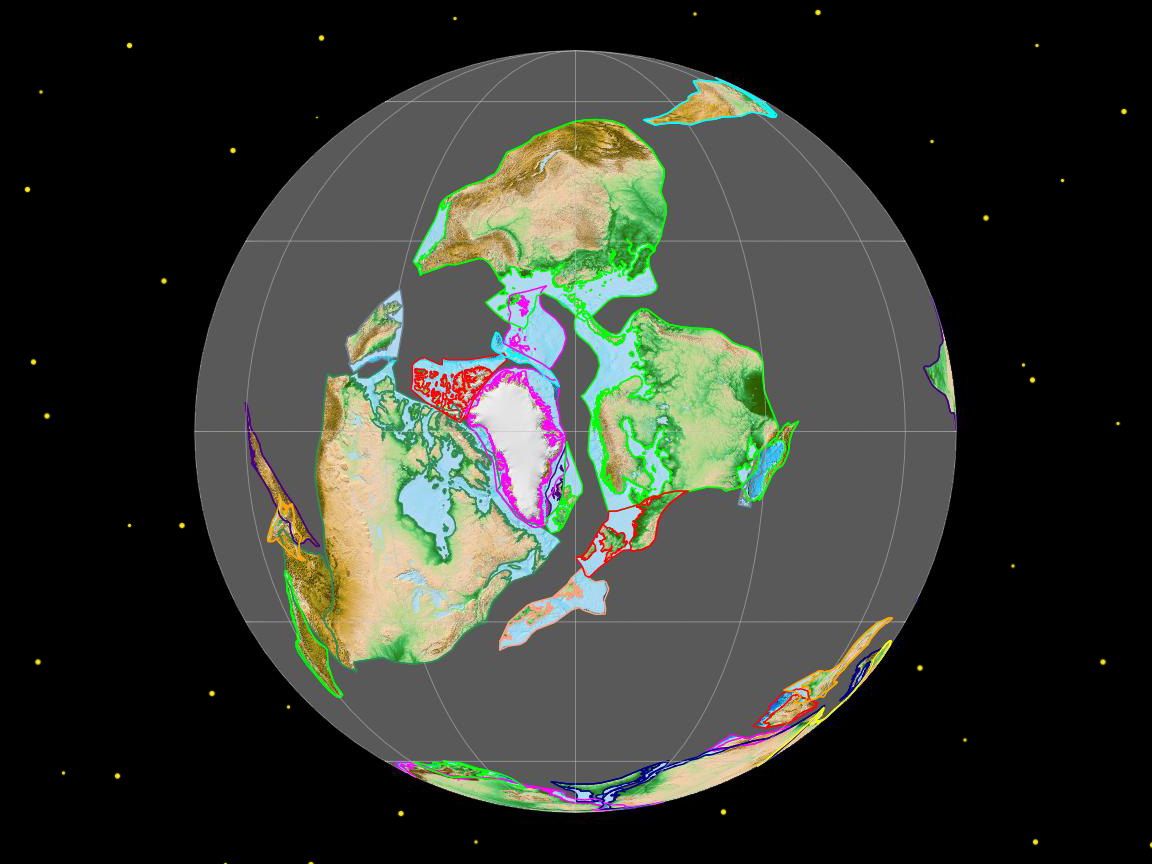
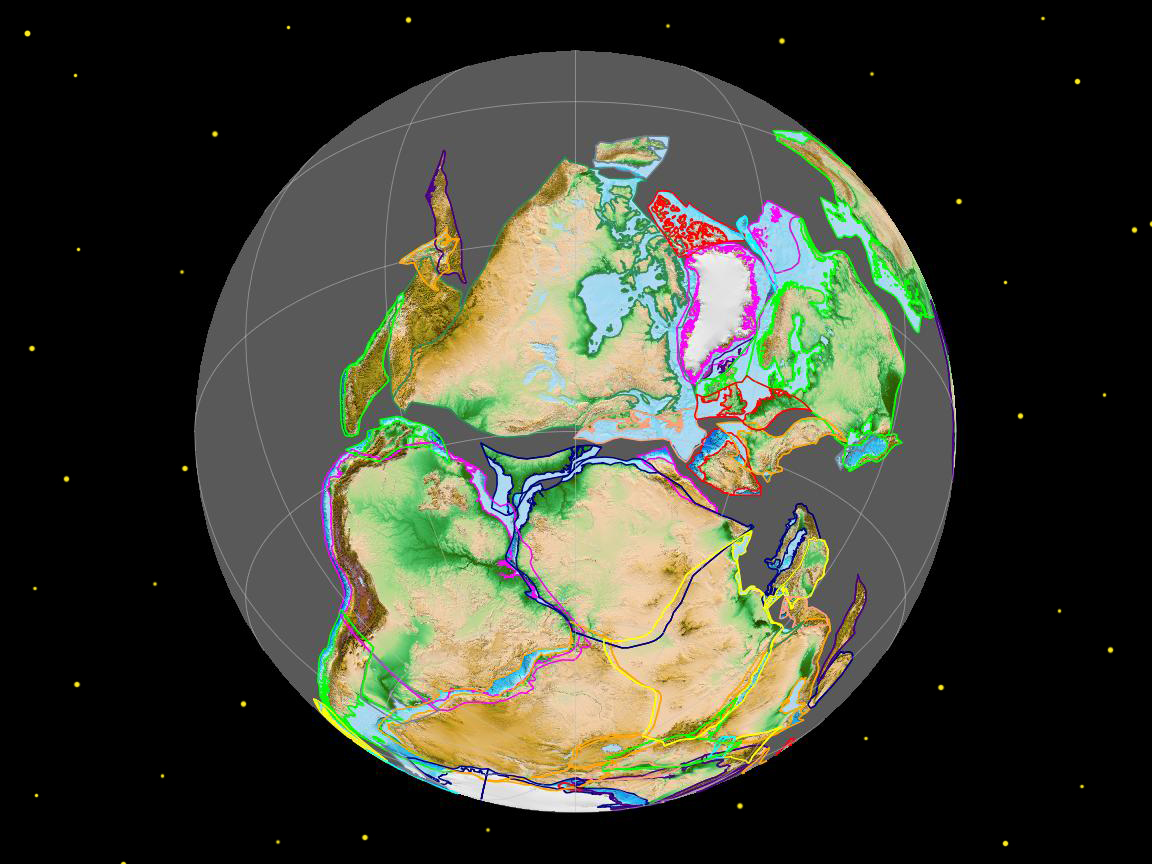
The Appalachian-Caledonian Orogeny stands as one of the most significant geological events in Earth’s history, shaping the landscapes of North America, Western Europe and Northwest Africa and leaving behind a rich tapestry of geological features. It began around 480 million years ago during the Ordovician period, as the ancient supercontinent of Gondwana collided with Laurentia and Baltica, leading to the formation of the Appalachian Mountains in North America, the Caledonian and Variscan Mountains in Europe, and the Anti-Atlas Mountains in Morocco.
Geology - Geological History
This collision initiated a series of complex tectonic interactions, including subduction, obduction, crustal thickening, and mountain building. As the continents converged, vast sedimentary deposits accumulated along the margins, providing valuable insights into the geological processes at play.
During the Silurian and Devonian periods, the convergence between Gondwana and Laurentia intensified, leading to the closure of the Iapetus Ocean and the subsequent collision of continental masses. This collision resulted in intense crustal deformation and uplift, giving rise to the ancestral Appalachian and Caledonian mountain ranges. The compression and folding of sedimentary layers led to the formation of vast mountain chains, characterized by towering peaks, deep valleys, and extensive fault systems.
Following the peak of mountain building during the Carboniferous period (c. 359 – 299 Mya), the Appalachian and Caledonian ranges underwent extensive erosion due to climatic influences and tectonic forces. Rivers, glaciers, and weathering processes gradually sculpted the landscape, carving out valleys, gorges, and sedimentary basins. Despite the erosion, remnants of the ancient mountain ranges persist today, serving as a testament to the geological forces that shaped the continents.
The Appalachian-Caledonian orogeny left a lasting imprint on the geological evolution of North America and Europe, influencing the distribution of resources, biodiversity, and geological features. The Appalachian Mountains, stretching from eastern Canada to Alabama in the United States, are renowned for their diverse geology and rich mineral deposits, contributing to the region’s economic prosperity. Similarly, the Caledonian Mountains in Europe, although heavily eroded, retain geological significance and serve as a foundation for understanding Earth’s tectonic history.
[Source: ChatGPT]