Draa Zagora is a region in southern Morocco, known for its stunning landscapes and
rich geological heritage. The geopark covers an area of approximately 6,100 square
kilometers and is home to a diverse range of geological features, including
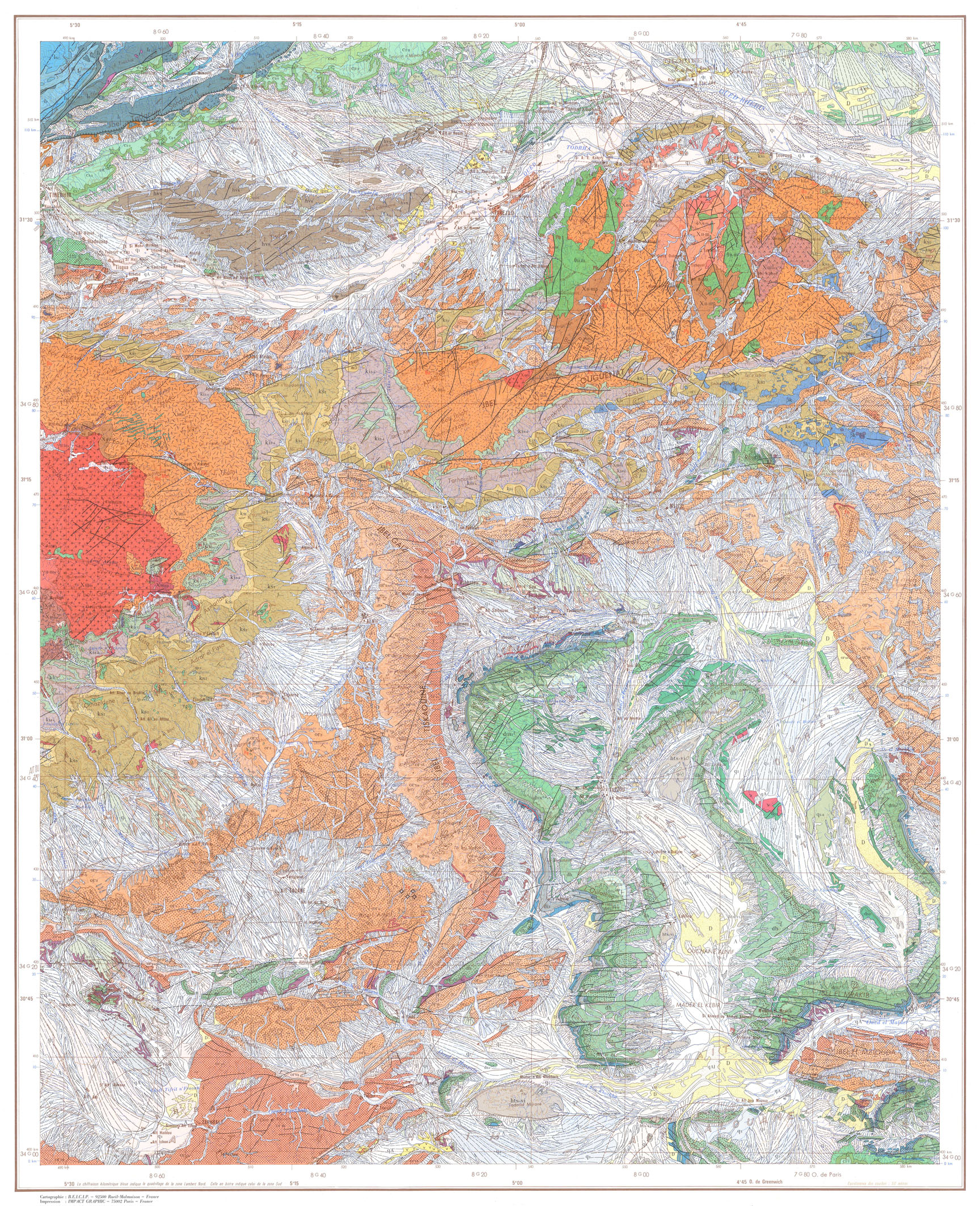
sedimentary rocks, volcanic formations, and mineral deposits. One of the most significant geological features in Draa Zagora is the Anti-Atlas Mountains, which were formed by a series of tectonic events that occurred over millions of years. The Anti-Atlas Mountains are characterized by towering peaks, deep gorges, and stunning natural landscapes that attract visitors from all over the world.
Draa Zagora Geopark
In addition to the Anti-Atlas Mountains, Draa Zagora is also home to several
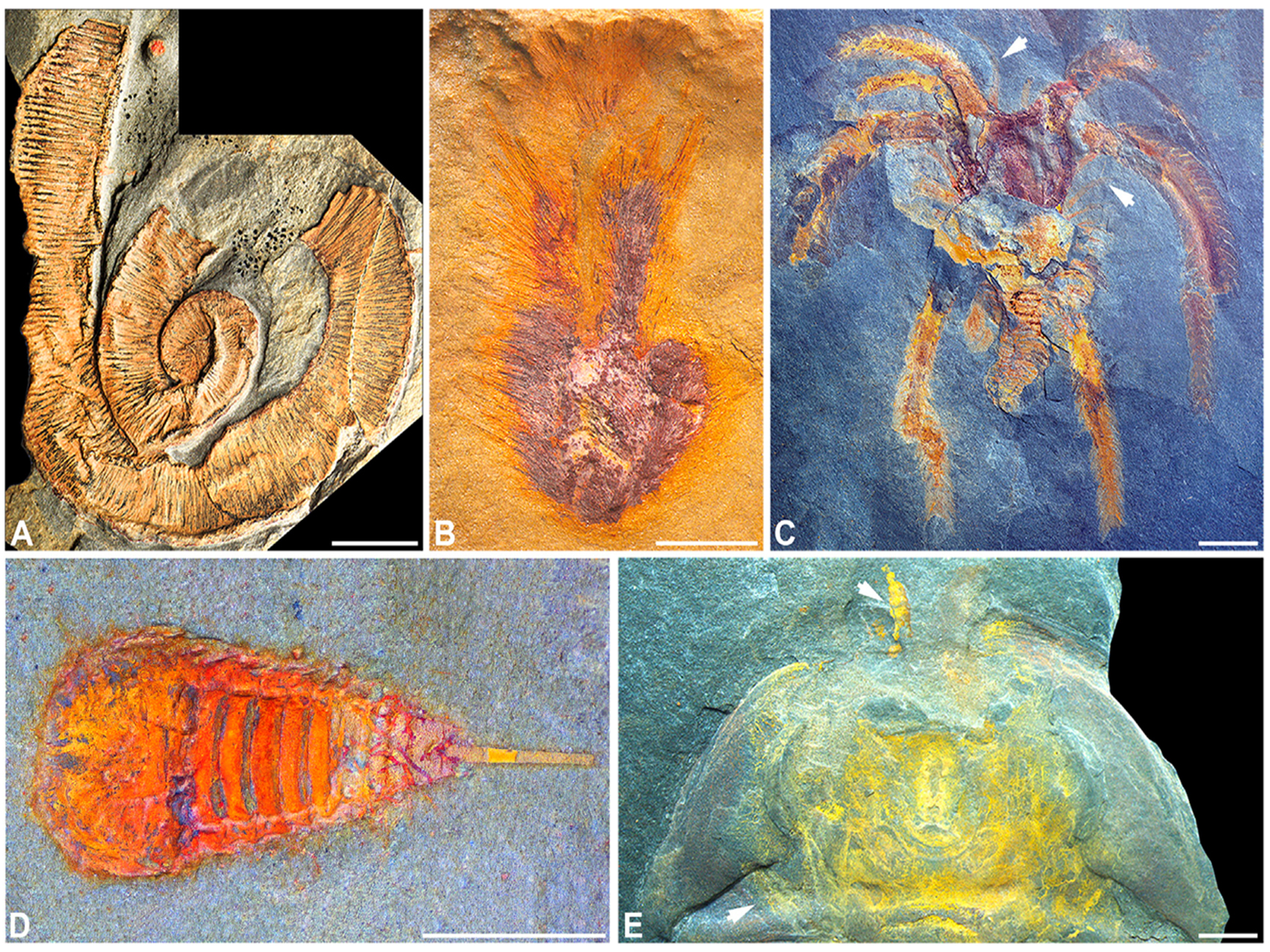
important geological sites, including the Fazouta formation one of the 100
international geological site with the exceptional conservation of Fossils, Ait
ouaazik, foum Chenna and Tidri which are prehistoric standing stones that date back to the Neolithic period.
The geopark is also home to a rich cultural heritage, with several traditional
Amazighs (Berber) villages located within its borders. These villages have
preserved their unique customs and traditions for centuries and offer visitors a
glimpse into Morocco’s rich cultural history. The Amazighs (Berbers) of the Draa Valley are known for their distinct language, culture, and way of life. They are traditionally nomadic or semi-nomadic and rely on animal husbandry and agriculture for their livelihoods. They also engage in crafts, such as weaving, pottery, and leatherwork, and cultural activities such as music, dance, and storytelling. They also have a strong tradition of oral poetry, which has been passed down through generations. The town of Zagora is known for its annual Festival of Amazigh Culture, which celebrates the cultural heritage of the Berber people.
Geology

Ecology

People